-
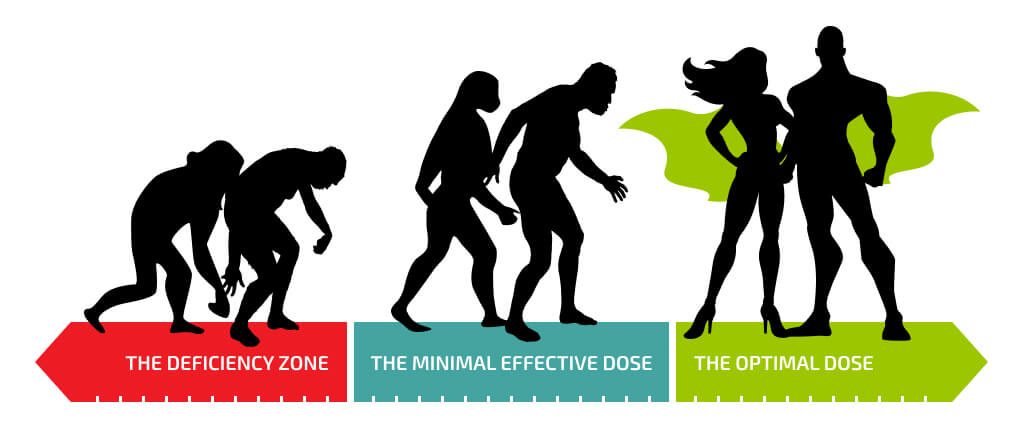
GET YOUR MAGNESIUM LEVEL TO THE OPTIMAL ZONE
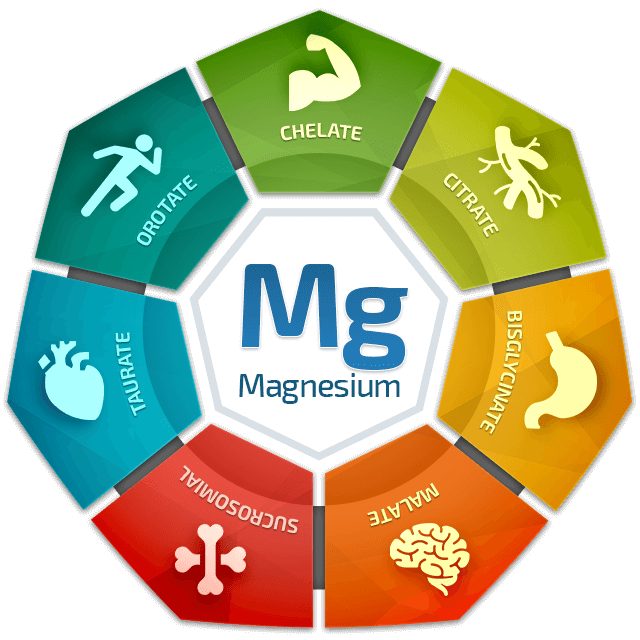
Why Getting ALL 7 Forms of Magnesium Transforms Your Stress & Performance
One of the biggest misconceptions about magnesium is that you just “need more” of it and you’ll be healthy and optimized.
But the TRUTH is, there are many different types of magnesium — and each plays a critical role in different functions in your body.
Most “healthy” people only get 1-2 forms at best (much of the population is deficient in all forms) — but when you get all 7 major forms of magnesium, that’s when the magic happens.
MAGNESIUM CHELATE
This form of magnesium is especially important for muscle building, recovery, and health.
MAGNESIUM CITRATE
Helps with the effects of obesity. In fact, one study found that this form helped arterial stiffness in healthy overweight individuals.
MAGNESIUM BISGLYCINATE
Often used to treat symptoms of excess stomach acid, such as stomach upset, heartburn, and acid indigestion.
MAGNESIUM MALATE
Some believe this to be the most bioavailable form of magnesium. It’s found naturally in fruits, giving them a “tart taste.”
Magnesium Malate can help with migraines, chronic pain, and depression.
MAGNESIUM ASPARTATE
This form helps the connection between your brain and muscles, your cardiac rhythms, and the overall acid-alkaline balance in your body. It also can support an elevated mood.
It is absolutely essential in the metabolism of macronutrients, as well as the utilization of other minerals, B-complex vitamins, vitamin C and vitamin E.
MAGNESIUM TAURATE
This is the form of magnesium best for your heart.
One study noted: “The complex magnesium taurate may thus have considerable potential as a vascular-protective nutritional supplement.”
MAGNESIUM OROTATE
While also helpful for the heart, magnesium orotate is believed to be the best form for metabolic improvements.
This makes it a favorite for athletes seeking enhanced recovery, energy and performance.
Description
Magnesium is one of the most important minerals for all aspects of health. It participates in over 600 different biochemical reactions in your body. Yet, over 80% of the population don’t get the minimum amounts of magnesium they need from diet alone because US soil is lacks it. Magnesium deficiency can increase all disease risks and keep you from performing optimally.
Even people who supplement with magnesium tend to take forms that are poorly absorbed, or they only take two forms at most. Each form of magnesium benefits different tissues and organ systems. If you’re only taking one or two forms, you’re most likely still deficient.
Magnesium Breakthrough is the only magnesium supplement on the market that is formulated to reach every tissue in your body to provide maximum health benefits and reverses low magnesium levels which could be causing health issues.
Magnesium Benefits
-
Promotes Heart Health
Magnesium is extremely important for heart health and blood vessel health. Magnesium deficiency seems to worsen the inflammation, blood vessel constriction, blood clotting, and stress responses that trigger heart conditions. Correcting magnesium deficiency appears to improve heart health and reduces risk of deaths, although it is unclear whether magnesium supplementation alone is sufficient to treat these conditions.
-
Improves the Ability to Deal With Stress and Helps to Relax
A magnesium supplement significantly reduced stress in people who are deficient in magnesium. Also, magnesium combined with vitamin B6 was 40% more helpful than magnesium alone for severe stress.
-
Helps With Mood, Cognitive Function, and Mental Health
A magnesium supplement (248 mg elemental magnesium) significantly improved mood after 2 weeks. Another trial found that magnesium supplements improved mood in seniors with type 2 diabetes.
-
Promotes Healthy Insulin Function and Promotes Healthy Metabolism
Magnesium is important for insulin to function well. Therefore, many people with insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome, and diabetes are deficient in magnesium. Even when the diabetes is well-controlled, magnesium supplement would still be necessary to achieve healthy magnesium levels. In a clinical trial involving 65 diabetes patients, magnesium supplementation promotes healthy insulin function and metabolism.
A large-scale systematic and dose-response analysis found that magnesium supplementation correlated with reduced body weight and waist circumference among specific groups of people. Those with insulin resistance, hypertension, obesity, magnesium deficiency, and women seem to weight less and had smaller waist circumference if they took magnesium supplements.
In pregnant women with gestational diabetes, magnesium supplementation improved blood glucose control and pregnancy outcomes.
-
Supports exercise performance and recovery
Magnesium supplementation improves speed and strength, possibly by making glucose metabolism more efficient. It also supports the necessary stress response to exercise, reduces muscle damage, and improves exercise recovery (400 mg/day, taken at breakfast).
-
Improves Sleep Quality
In a small clinical trial involving 46 elderly subjects with insomnia, 500 mg of daily magnesium supplement reduced insomnia scores, sleep latency, and cortisol. Subjects who took the magnesium also had more serum melatonin, slept deeper, and were less likely to wake up in the middle of the night.
-
Builds Stronger Bones
Magnesium is a key building blocks of your bones. Magnesium deficiency can contribute to osteoporosis by:
- preventing healthy bone formation, creating brittle bones
- causing low-grade inflammation
- Increasing cortisol, which can contribute to bone loss
- reducing parathyroid hormone
In a clinical trial involving 73,684 postmenopausal women, low magnesium intake was associated with lower bone density in the hip and whole body. Magnesium intake slightly higher than the Recommended Dietary Allowance was associated with lower arm and wrist factures from falling.
-
Promotes Healthy Blood Pressure
A meta-analysis of 34 randomized control trials found that magnesium reduced blood pressure. However, the effect size is clinically small (<2 mmHg) [R]. Therefore, magnesium might be good for supporting overall health and healthy blood pressure, but you may also need other interventions to achieve healthy blood pressure levels.
-
Promotes Balanced and Healthy Immune System.
Magnesium deficiency increases inflammation. In a meta-analysis involving 32,198 people, those with more magnesium had less serum C-reactive protein (a marker of inflammation).
Overall, magnesium deficiencies tend to exacerbate or increase the risk of conditions that involve chronic inflammation.
-
Supports Vitamin D Activation and Metabolism
Both Vitamin D and magnesium have important roles in bone health, immune function, and metabolism. Magnesium is a cofactor in vitamin D conversion and activation. Some people cannot increase their blood 25-hydroxy vitamin D levels despite supplementing with vitamin D3 because they are deficient in magnesium. In other words, magnesium deficiency can make vitamin D ineffective.
Also, in people deficient in magnesium, high doses of vitamin D3 could worsen magnesium deficiency and increase the potential for side effects of vitamin D3, such as having calcium deposits in the arteries.
How To Take Magnesium
When you take magnesium in the morning, it supports brain function and stress response throughout the day. In the evening, high doses of magnesium promote relaxation and may help with sleep. Therefore, it is best to divide your magnesium supplement doses throughout the day. If that is not possible, take magnesium whenever you can.
It is better to take mineral supplements, such as magnesium, on an empty stomach because you will absorb it more efficiently. However, some people experience upset stomach, so they take it with food.
Studies of inorganic magnesium salts (magnesium oxide, chloride, and sulfate) found that stomach acid is necessary for magnesium absorption, so they need to be taken on an empty stomach. However, organic magnesium salts (citrate, glycinate, chelate, etc) are more readily absorbed even when taken with food.
Our bodies don’t store magnesium well. It is generally excreted from your system within 24 hours of intake. Therefore, it is important to take magnesium every day.
Magnesium And Anxiety
Magnesium is extremely important for mental and neurological health. Studies have shown that magnesium deficiency causes animals to be stressed and anxious. In humans, a low-magnesium diet is associated with anxiety and depression. You need magnesium to deal with stress. Stress causes you to excrete more magnesium through urine Therefore, being deficient in magnesium can create anxiety.
Magnesium supplementation has been shown to promote a healthy stress response and reduce neurotransmitters that cause anxiety. It also promotes relaxation by increasing GABA, the calming neurotransmitter
In a randomized controlled trial of mildly anxious subjects, magnesium + vitamin B6 significantly reduced stress scores compared to the placebo
Magnesium supplements have also been shown to help improve mental health in women with premenstrual syndrome and postpartum anxiety
To boost mood, reduce anxiety, and promote a healthy stress response, it is best to use a combination of forms of magnesium combined with vitamin B6. Studies have confirmed that magnesium with organic acid salt (e.g. citrate and malate) or amino acids (e.g. taurate, glycinate, and aspartate) are significantly better absorbed than inorganic salts (oxide, chloride, and sulfate). Also, these different forms of magnesium are absorbed into different tissues, with taurate, malate, and citrate being the most beneficial for the nervous system
Magnesium breakthrough contains all 7 forms of the most bioavailable magnesium along with vitamin B6 to support mental health and promote a healthy stress response.
Scientific Studies
- Multum, C. (n.d.). Chelated Magnesium. Drugs.Com. https://www.drugs.com/mtm/chelated-magnesium.html#moreResources
- Schutten, J. C., Joris, P. J., Mensink, R. P., Danel, R. M., Goorman, F., Heiner-Fokkema, M. R., Weersma, R. K., Keyzer, C. A., de Borst, M. H., & Bakker, S. (2019). Effects of magnesium citrate, magnesium oxide and magnesium sulfate supplementation on arterial stiffness in healthy overweight individuals: a study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials, 20(1), 295. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13063-019-3414-4
- Drugs & Medications. (n.d.). Magnesium Glycinate Tablet WebMD. https://www.webmd.com/drugs/2/drug-152090/magnesium-glycinate-oral/details
- Uysal, N., Kizildag, S., Yuce, Z., Guvendi, G., Kandis, S., Koc, B., Karakilic, A., Camsari, U. M., & Ates, M. (2019). Timeline (Bioavailability) of Magnesium Compounds in Hours: Which Magnesium Compound Works Best?. Biological trace element research, 187(1), 128–136. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-018-1351-9
- Chouinard, G., Beauclair, L., Geiser, R., & Etienne, P. (1990). A pilot study of magnesium aspartate hydrochloride (Magnesiocard) as a mood stabilizer for rapid cycling bipolar affective disorder patients. Progress in neuro-psychopharmacology & biological psychiatry, 14(2), 171–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/0278-5846(90)90099-3
- McCarty M. F. (1996). Complementary vascular-protective actions of magnesium and taurine: a rationale for magnesium taurate. Medical hypotheses, 46(2), 89–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0306-9877(96)90007-9
- Rosenfeldt F. L. (1998). Metabolic supplementation with orotic acid and magnesium orotate. Cardiovascular drugs and therapy, 12 Suppl 2, 147–152. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1007732131887
-